A telegraph code is one of the character encodings used in telegraphic communication. Morse code is the most well-known example.
Telegraphy generally refers to the electrical telegraph, however optical telegraph systems were in operation before that.
A code is made up of a number of code points, each of which corresponds to a letter of the alphabet, an integer, or another character.
Telegraphy is an old method of sending communications across large distances using Morse code. Initially, wires were utilized to transmit electrical impulses, and subsequently, radio transmissions were employed.
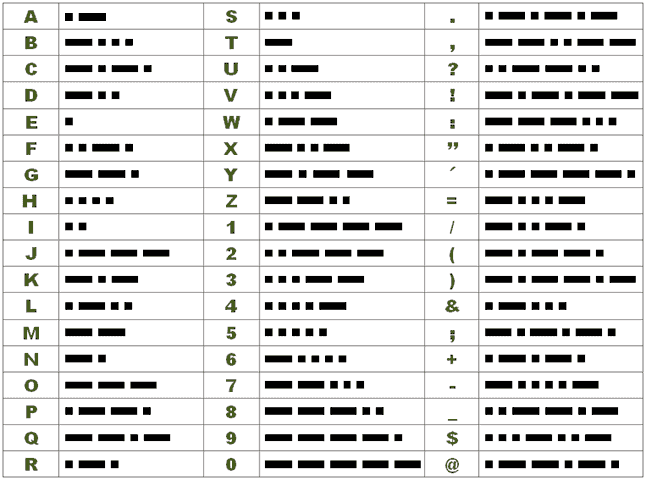
For instance, Morse code for E, the most common letter in English, is a single dot ( ▄ ), whereas Q is ▄▄▄ ▄▄▄ ▄ ▄▄▄
Morse Code Symbols
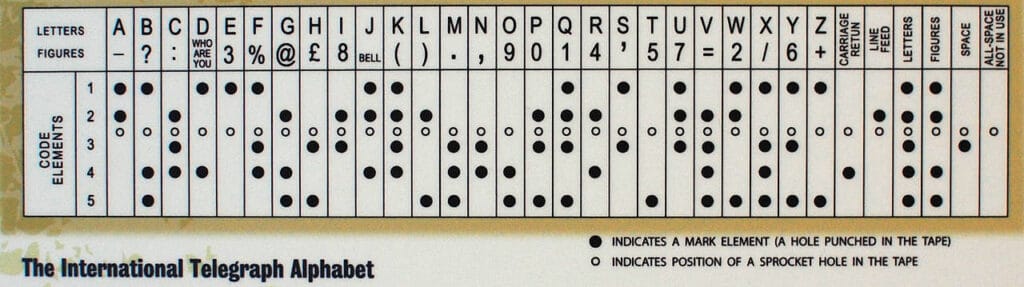
Telegraphy Symbols
| Symbol | Description | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Telegraph equipament Electrical telegraph |  | Telegraph equipament Electrical telegraph Generic symbol |
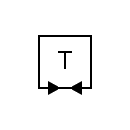 | Duplex telegraph | 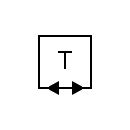 | Two-way simplex telegraph |
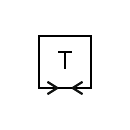 | Duplex telegraph | 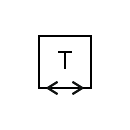 | Two-way simplex telegraph |
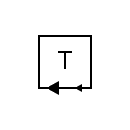 | Telegraph receiver device | 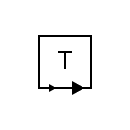 | Telegraph transmitter device |
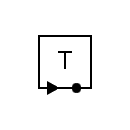 | Telegraph receiver | 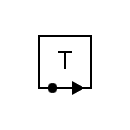 | Telegraph transmitter |
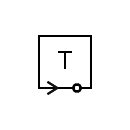 | Telegraph receiver | 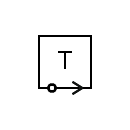 | Telegraph transmitter |
Telegraph Key
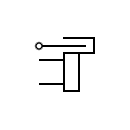 | Telegraph signal key |  | Telegraph key |
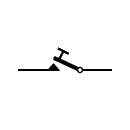 | Hand key |  | Hand key |
Reference:

